Ettercap🕵️: Intercept Passwords☠️ with ARP-Spoofing😈
- alvin gitonga
- Dec 3, 2022
- 6 min read
CyberMorans,

ARP spoofing is an attack against an Ethernet or Wi-Fi network to get between the router and the target user😱 In an ARP-spoofing attack, messages meant for the target are sent to the hacker😈 instead, allowing the hacker to spy on, deny service to, or man-in-the-middle the target 💀
One of the most popular tools for performing this attack is Ettercap, which comes preinstalled on Kali Linux😎

Types of ARP Spoofing Attacks
There can be three primary outcomes after an hacker gains initial success in poisoning the ARP cache of other hosts on the network:
👉 The hacker can spy on traffic: seeing everything that the target user does on the network. It's straight forward☺️
👉 The hacker can man-in-the-middle: They can intercept passwords typed into an HTTP website, see DNS requests, and resolve IP addresses the target is navigating to in order to see what sites the target is visiting. In a man-in-the-middle attack, the hacker can not only to see what's happening on the network but manipulate it as well🧐 Por examp, they can attempt to downgrade the encryption the connection is using by deliberately requesting insecure versions of webpages to make the attacker's job of sniffing passwords easier. Also, a hacker can simply be a nuisance. Like, they can replace words in the text of a website, flip or replace images 🥸, or modify other types of data flowing to and from the target.
👉 The hacker can perform denial-of-service attack: This is the most frustrating to a target. While a Wi-Fi authentication attack is by far the more common cause of a Wi-Fi network being attacked, ARP spoofing can be much more challenging to figure out🧐 If the attacker chooses not to forward on the packets now being sent to it instead of the target, the target will never receive them. The Wi-Fi network can be jammed from the inside, getting between the target and the router and then dropping the packets flowing between😎
Unlike many of the programs that are command-line only, Ettercap features a graphical interface that's very beginner-friendly☺️ While the results may sometimes vary, Ettercap is an excellent tool for newbies to get the hang of network attacks like ARP spoofing🙊 If you don't already have it (you downloaded a lite version of Kali), you can get it by typing into the terminal 👇
# apt install ettercap-graphical
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
ettercap-graphical is already the newest version (1:0.8.2-10+b2).Ettercap isn't the only tool for this, nor is it the most modern. Other tools, such as Bettercap, claim to do what Ettercap does but more effectively 😜
The general workflow 🚋 of an Ettercap ARP spoofing attack is to join a network you want to attack, locate hosts on the network, assign targets to a "targets" file, and then execute the attack on the targets😋
After all that, we can metaphorically watch over the target's shoulder as they browse the internet, and we can even kill the connection from websites we want to steer them away from🤫 We can also run various payloads, like isolating a host from the rest of the network, denying them service by dropping all packets sent to them, or running scripts to attempt to downgrade the security of the connection☠️
So, lets do this💪

🚀Connect to the Network
The first step of ARP spoofing is to connect to the network you want to attack. If you're attacking an encrypted WEP, WPA, or WPA2 network, you'll need to know the password. This is because we're attacking the network internally, we need to be able to see some information about the other hosts on the network and the data passing within it🤫
You can connect to a network for ARP spoofing in two ways. The first is to connect via Ethernet, which is very effective but is rarely subtle💩 Instead, many people prefer to use a wireless network adapter and perform the ARP spoofing over Wi-Fi.
🚀Start Ettercap
In Kali, click on "Applications," --> "Sniffing & Spoofing," --> "ettercap-graphical." Alternatively, click on the "Show Applications" option in the dock, then search for and select "Ettercap"👇

make sure you have an active connection to the network to continue.
🚀Choose Network Interface to Sniff 👃
Click on the "Sniff" --> "Unified sniffing"
A new window will open asking you to select which network interface you want to sniff on. Select the network interface currently connected to the network you're attacking 👇
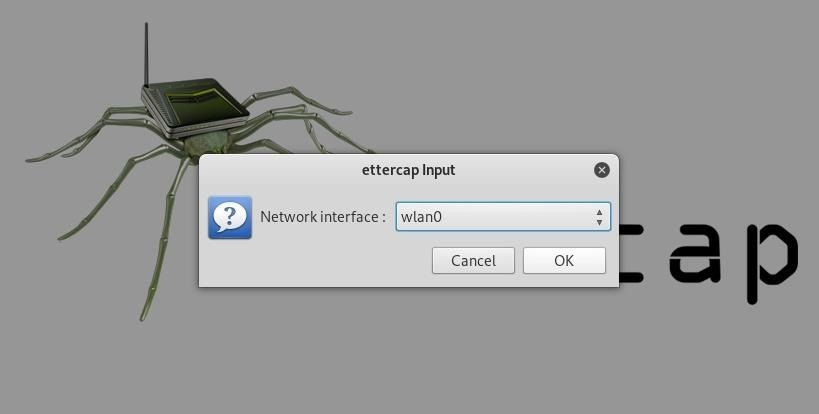
You'll see some text confirming that sniffing👃 has started, and you'll be able to access more advanced menu options such as Targets, Hosts, Mitm, Plugins, etc. Before we get started using any of them, we'll need to identify our target on the network 👇

🚀Identify Hosts on a Network
To find the device we want to attack on the network, Ettercap has a few tricks up its sleeve. First, we can do a simple scan for hosts by clicking "Hosts," --> "Scan for hosts."
A scan will execute, and after it finishes, you can see the hosts Ettercap has identified on the network by clicking "Hosts," --> "Hosts list" 👇
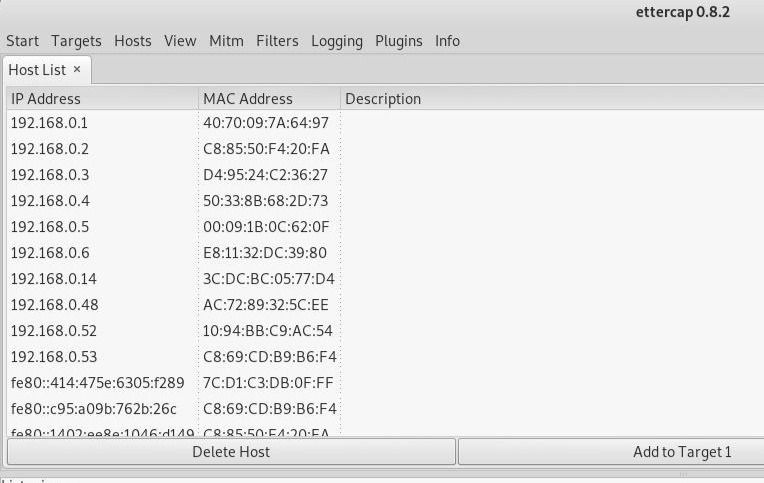
We can see👆 a list of targets discovered on the network. To see what they're doing or narrow down the targets? Click on "View," --> "Connections" to start snooping on connections.
Once in the "Connections" view, you can filter the connections by IP address, type of connection, and whether the connection is open, closed, active, or killed. This gives you a lot of snooping power, which can be augmented by clicking the "View," --> "Resolve IP addresses."
This means Ettercap will try to resolve the IP addresses it sees other devices on the network connecting to 👇
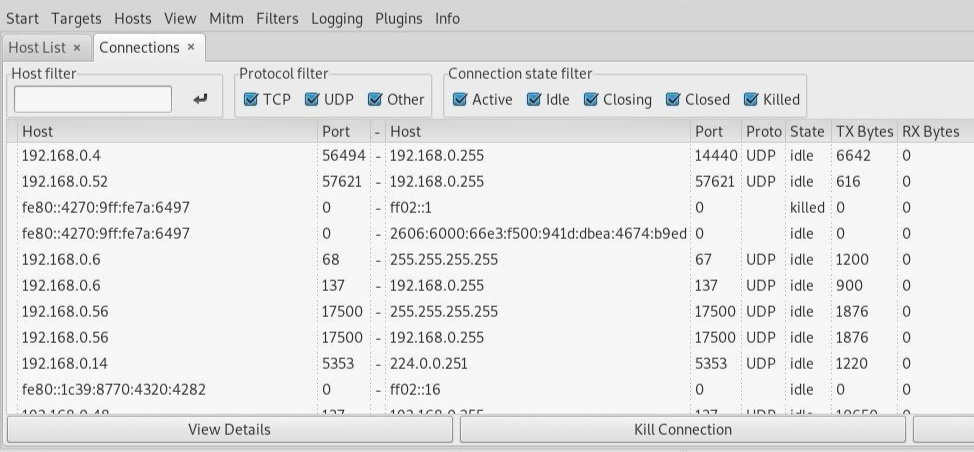
PS: Should you want to identify a target on a network and know what they're browsing, look over their shoulder at the website they're on, and match the website to an IP address with an active connection to the same website. Otherwise, you can usually tell by the MAC address, as you can look it up online to see the manufacturer😋
🚀Choose a Target with ARP Spoofing
Now that we've identified our target's IP address, it's time to add them to a target list. This will be telling Ettercap that we want to designate that IP address as one we want to pretend to be, so that we're receiving messages from the router that were meant to be sent to the target.
PS: (MiTM) Imagine calling the cops but instead the call gets redirected to me, the burgler🤨
Go back to the "Hosts" screen, and select the IP address of the target you want to target.
Click the IP address to highlight it, then click on "Targets," --> "Target list," to see a list of devices that have been targeted for ARP spoofing 👇
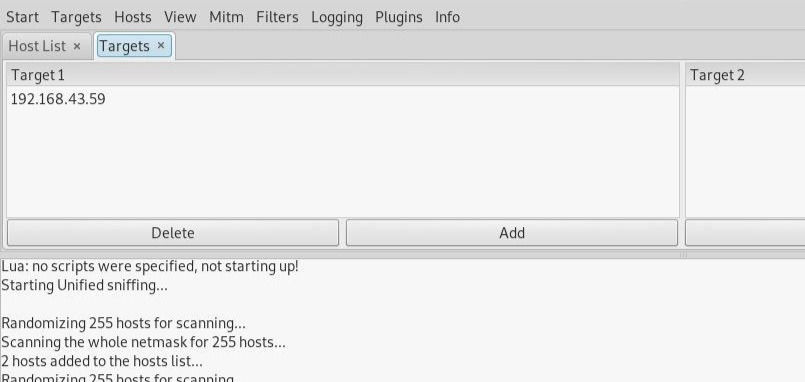
Now, we can go to the "Mitm" menu to start our attack on this target.
🚀Attack the Targets
Click on the "Mitm" menu --> "ARP poisoning." A popup will open, select "Sniff remote connections" to begin the sniffing👃 attack 👇
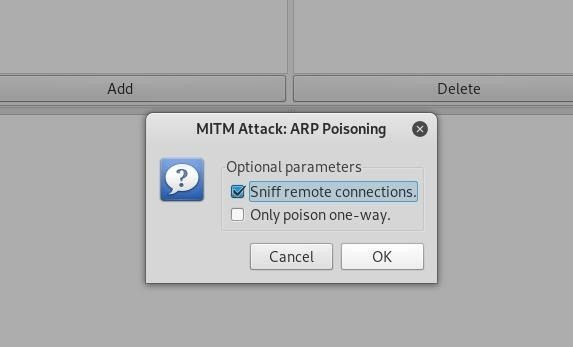
Once this👆 attack has begun, you'll be able to intercept login credentials if the user you're targeting enters them into a website that doesn't use HTTPS. This could be a router, device on the network or even a website that uses poor security💩
To try another attack, you can click on "Plugins," --> "Load plugins," to show the plugin menu. If you select the DOS attack, it will begin dropping the packets sent to this target, cutting off their internet access 👇
🚀Try Intercepting a Password
Now, let's actually try intercepting a password😋 A website that's great for testing your web hacking skills is aavtain.com, which deliberately uses bad security so that you can intercept credentials and some🛰️ On the target device, navigate to aavtrain.com. Once it loads, you'll see a login screen you can enter a fake login and password 👇
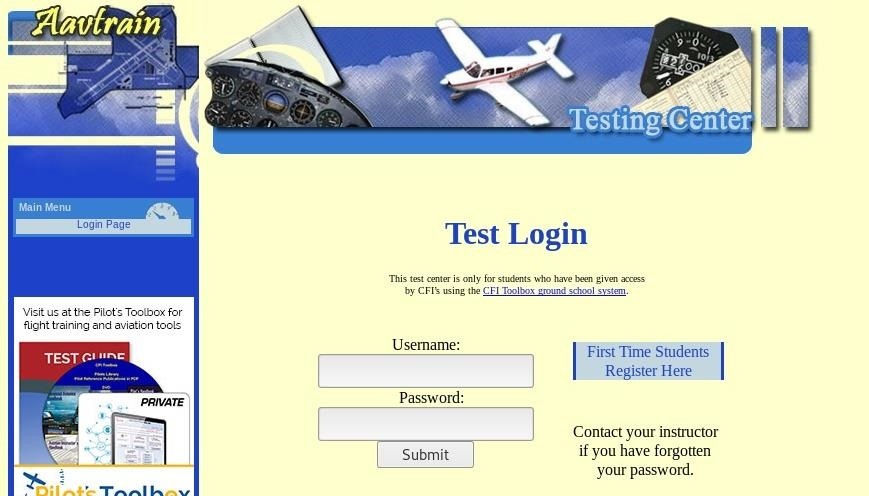
👆 Enter a username and password, then hit "Submit" If Ettercap is successful, you should see the login and password you typed appear on the attacker's screen!
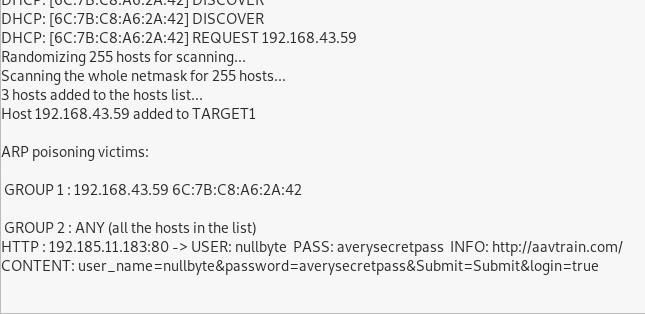
👆 We can see that Ettercap successfully ARP poisoned the target and intercepted an HTTP login request the target was sending to an insecure website😝

🚀Some Limitations
The limitation of ARP spoofing is that it only works if you're connected to a Wi-Fi network. This means it works on open networks but may not work well against networks that have more sophisticated monitoring or firewalls that may detect this sort of behavior☹️
ARP spoofing attacks are another example of why it's so essential to have strong passwords for your networks and limit access to those you trust. You're giving away a lot of trust when you give someone your network password or an Ethernet connection, so remember to pick your passwords carefully and who you share them with😄
🚀Conclusion 🤖
Subscribe to receive notifications of similar posts 😜 where we will be reverse engineering malware, vulnerabilities as well as hacking vectors, stories, tutorials and other Infosec stuff...😋
Follow me on twitter for daily Infosec Memes and shenanigans😝
Morans,

Thank you for your time, Like and leave a comment/review and as always, stay awesome! 😋👊 💪




Comments